Weingarten competency framework
The rapid pace of digital transformation not only changes our daily life, but also has profound effects on education. In order to prepare teachers for the requirements of future teaching environments the transfer of digital competencies is essential.
The Weingarten competency framework of digital skills for teachers builts up on those requirements and serves as a comprehensive foundation which is based on the DigCompEdu framework.
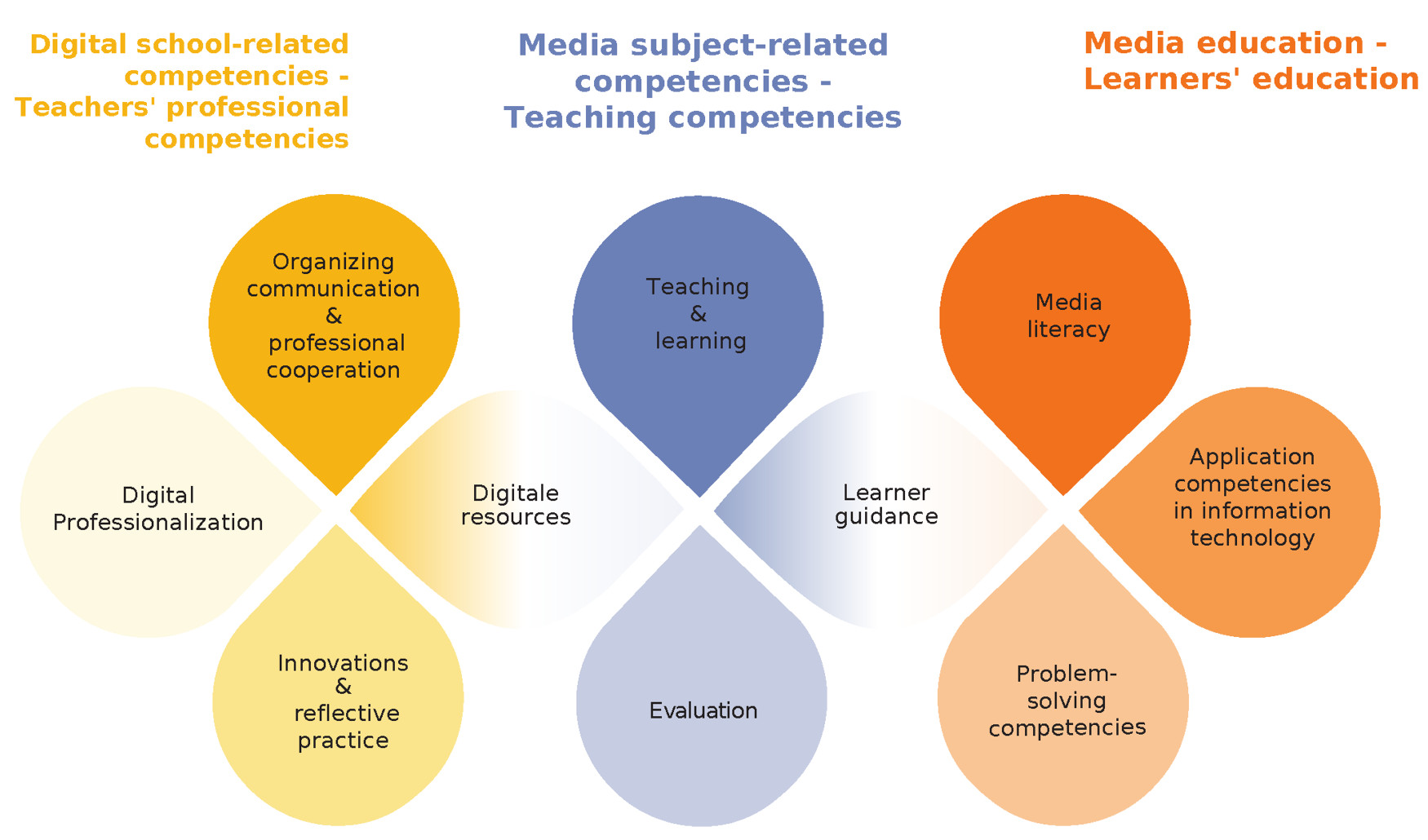
The model consists of 3 competencies (“digital school-related competencies”, “media subject-related competencies” and “media education” as well as their overlaps), which are divided into 10 sub-areas. These sub-areas comprise a total of 152(4) individual competencies with their respective title of competencies and description of competencies. The 152(4) competencies are divided into the three-part “basic competencies”, “detail competencies” and “advanced competencies”. The basic competencies are a mixture of competencies, which are at different taxonomy levels (knowledge, application, further development). The university of education Weingarten has derived 8 abstract competencies for its course manual.
This framework is specially designed to serve as a sound basis for the design and implementation of courses, with the aim of equipping prospective teachers both theoretically and practically for an efficient and ethically responsible use of digital technologies in teaching.
| Weingarten competency framework divided into 10 sub-areas |
|---|
Framework description
Within the area of “digital school-related competencies”, the focus is on enabling prospective teachers to use digital media for professional communication with learners, parents and non-school stakeholders, for cooperation within the school community, for their own professional development and for digital school development in a contextual-based and goal-oriented manner.
In the area of “media subject-related competencies”, prospective teachers are enabled to systematically integrate digital media into their own lessons and thereby unleash the full potential for their own subject.
In “media education”, the focus is on promoting learners' digital-related competencies. Prospective teachers can guide and support learners in their development in the reflective and responsible use of digital media.
10 sub-areas (e.g. innovation & reflective practice) with overlaps (“digital resources” and “learner guidance”) are assigned to the 3 areas of competence. The competencies fall under these ten sub-areas, each of which was assigned to only one taxonomy level in order to make the model applicable and testable in teaching.